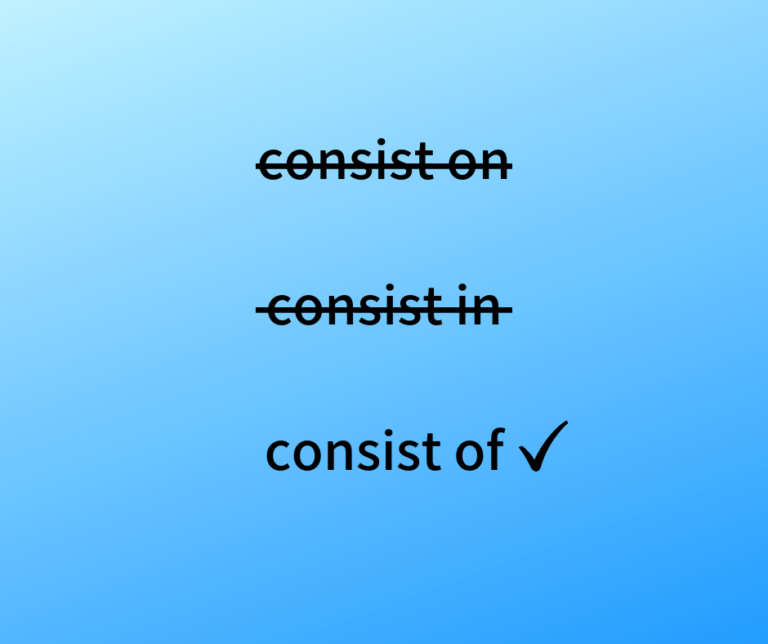
How to Use a Prepositional Phrase
Prepositions have a lot of power in the English language! They can provide more details about the location of an object, the time an action takes place, the direction a subject is moving, where something is located, and more!
For English language learners, it can be a challenge deciding which preposition to use, when to use it, and how to use it in order to express exactly what you are trying to say. While there are many aspects to proper preposition use, here we will look at strategies for forming prepositional phrases. This will ultimately help improve your ability to speak more precisely.
A prepositional phrase starts with a preposition (i.e., in, at, on, etc.) and is followed by a noun or noun phrase. This is called the object of the preposition.
See also: 100+ IN and ON Collocations
Examples:
1) The cat sits on the mat.
2) I usually have breakfast before work.
3) I will see you at nine o’clock.
Sometimes you’ll want to use a gerund to complete a prepositional phrase if the verb in that phrase is functioning as a noun. Remember, the gerund form is the base verb + ing!
See also: 5 Commonly Confused Preposition Collocations
Examples:
1) Matthew focused on completing his homework before class.
2) She was excited about going on a vacation to Hawaii.
3) She succeeded in overcoming her fear of heights by slowly ascending the ladder.
Remember the object of the preposition that we talked about earlier? Some sentences will require you to use pronouns (I, you, he, she, it, we, they) within that object. In this situation, you must use the object form of that pronoun (i.e., me, you, him, her, it, us, them).
Examples:
1) The book is for him to read during his vacation.
2) She gave the flowers to me after the performance.
3) The teacher asked us for our opinions on the topic.
There are many verbs and prepositions commonly paired together, so you’ll often use prepositional phrases after verbs to explain more about that action.
Examples:
1) I agree with you that we need a better plan.
2) Frank was concerned about the weather.
3) That car belongs to me.
Prepositional phrases can also act like adjectives by modifying nouns. Likewise, they can act like adverbs by modifying adjectives and verbs.
Examples:
1) That bird in the sky is beautiful. (Modifies the noun “bird”)
2) She was enchanted by the red roses. (Modifies the adjective “enchanted”)
3) Kelly took care of the horses. (Modifies the verb “took care”)
You can even use prepositional phrases to give more information about other prepositional phrases!
Examples:
1) Robert went to work at 8:00 am.
2) She left her shoes on the floor in the laundry room.
Try practicing prepositional phrases through listening activities. Next time you’re watching a TV show in English, see if you can count how many prepositional phrases you hear, and note if there are any verb/preposition combinations that are repeated. Write those down and try creating your own sentences with them!